一共五道,这次比第一次更惨…
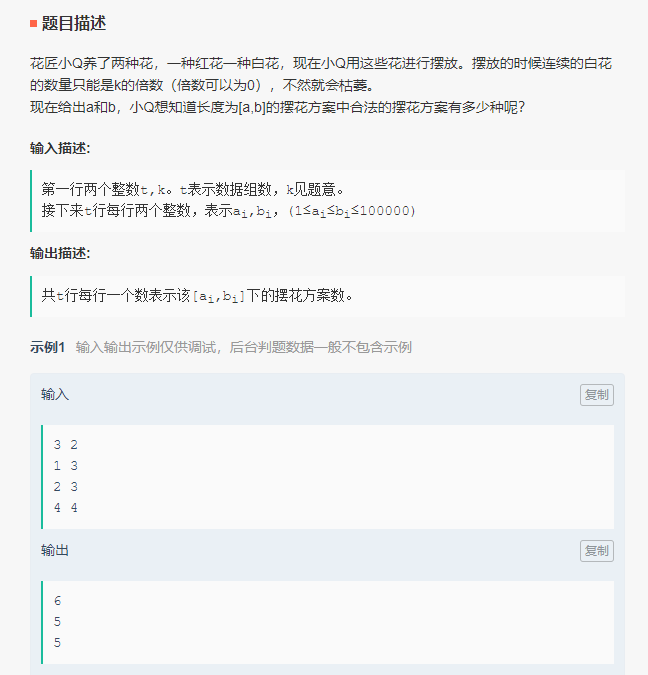
第一道:
本题尝试去进行找规律,发现规律如下:
若总共要种n株花,其中k株白花,因为白花必须连续且位k的倍数(对题目的误解),故会有n-k+1种方案。以下代码为50%。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//总共需要种花n株,其中有k株是白花
int Fun(int n, int k) {
int res;
if (k == 0)
res = 1;
else
res = n - k + 1;
//cout << n << "株花" << k << "株白花的方案有" << res << "种" << endl;
return res;
}
int main(void)
{
int t, k;
cin >> t >> k;
for (int i = 0; i < t; ++i) {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
int count = 0;
for (int j = a; j <= b; ++j) {
for (int n = 0; n <= j; n += k) {
count += Fun(j, n);
}
}
cout << count << endl;
}
return 0;
}
分析其错误原因:原题的意思是连续的白花的数量只能是k的倍数,即对于共种5株花,其中4朵白花(k为2),这种情况下,以上思路会漏了一种情况:白白红白白。
正确解法应使用动态规划进行计算。
第二道:
对命令模式不了解:https://blog.csdn.net/zhengzhb/article/details/7550895(点击链接查看命令模式)
原代码框架如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 完成以下各个类的实现,可以自由的增删函数
/**
* 终端操作上下文环境
*/
class TerminalEnv {
private:
string m_curdir;
public:
};
class Command {
public:
virtual ~Command() {}
virtual bool execute ( TerminalEnv& env ) = 0;
virtual bool undo ( TerminalEnv& env ) {
return true;
}
};
class AddDirCommand : public Command {
public:
bool execute ( TerminalEnv& env ) {
}
bool undo ( TerminalEnv& env ) {
}
};
class CDCommand : public Command {
bool execute ( TerminalEnv& env ) {
}
bool undo ( TerminalEnv& env ) {
}
};
class AddFileCommand : public Command {
bool execute ( TerminalEnv& env ) {
}
bool undo ( TerminalEnv& env ) {
}
};
int main() {
int m;
cin >> m;
for ( int i = 0; i < m; ++i ) {
// 处理各个命令
}
return 0;
}
尝试写了一下,感觉似乎写复杂了?测试案例通过。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
// 完成以下各个类的实现,可以自由的增删函数
/**
* 终端操作上下文环境
*/
class Node {
public:
Node(string name, int type) {
_name = name;
_type = type;
}
int GetType() {
return _type;
}
string GetName() {
return _name;
}
//在该目录下添加文件或文件夹
void AddItem(Node *c) {
if (c->GetType() == 0)
SetChildDir(c);
else
SetChildFile(c);
c->SetParent(this);
}
//移除文件或文件夹
void Remove(Node *c) {
if (c->GetType() == 0)
RemoveDir(c);
else
RemoveFile(c);
}
//查找是否存在某文件,若不存在返回空指针
Node* FindFile(string fileName) {
for (auto it : _childrenFile) {
if (it->GetName() == fileName)
return it;
}
return NULL;
}
//查找是否存在某文件夹,若不存在返回空指针
Node* FindDir(string dirName) {
for (auto it : _childrenDir) {
if (it->GetName() == dirName)
return it;
}
return NULL;
}
//查找上一层目录
Node* FindParent() {
return _p;
}
~Node() {
_childrenDir.clear();
_childrenFile.clear();
delete _p;
}
private:
string _name;
//0代表文件夹,1代表文件
int _type;
//指向当前目录底下的文件夹
vector<Node*> _childrenDir;
//指向当前目录底下的文件
vector<Node*> _childrenFile;
//指向当前目录的上层目录
Node* _p;
//设置上一层目录
void SetParent(Node *p) {
_p = p;
}
//设置子目录
void SetChildDir(Node *c) {
_childrenDir.push_back(c);
}
//设置该目录下的文件
void SetChildFile(Node *c) {
_childrenFile.push_back(c);
}
//移除该目录下的某个文件
void RemoveFile(Node *c) {
vector<Node*>::iterator it;
for (it = _childrenFile.begin(); it != _childrenFile.end(); it++)
{
if (*it == c) {
_childrenFile.erase(it);
return;
}
}
}
//移除该目录下的某个文件夹
void RemoveDir(Node *c) {
vector<Node*>::iterator it;
for (it = _childrenDir.begin(); it != _childrenDir.end(); it++)
{
if (*it == c) {
_childrenDir.erase(it);
return;
}
}
}
};
//打印完整路径
void LogPath(Node* n) {
stack<Node*> s;
Node* p = n;
while (p != NULL)
{
s.push(p);
p = p->FindParent();
}
cout << s.top()->GetName();
s.pop();
if (s.size() == 0)
return;
while (s.size() > 1)
{
cout << s.top()->GetName() << "/";
s.pop();
}
cout << s.top()->GetName();
}
class TerminalEnv {
private:
string m_curdir;
Node* m_curDir;
public:
TerminalEnv() {
m_curdir = "/";
m_curDir = new Node("/", 0);
}
//获取当前路径名称
string GetCurDirName() { return m_curdir; }
//添加文件
void AddFile(string fileName) {
Node* tmpNode = new Node(fileName, 1);
m_curDir->AddItem(tmpNode);
//输出文件全路径
LogPath(tmpNode);
cout << endl;
}
//查看当前文件是否已存在
bool IsFileExit(string fileName) {
Node* n = m_curDir->FindFile(fileName);
if (n != NULL)
return true;
else
return false;
}
//添加文件夹
void AddDir(string dirName) {
Node* tmpNode = new Node(dirName, 0);
m_curDir->AddItem(tmpNode);
//输出文件全路径
LogPath(tmpNode);
cout << "/" << endl;
}
//查看当前文件夹是否已存在
bool IsDirExit(string dirName) {
Node* n = m_curDir->FindDir(dirName);
if (n != NULL)
return true;
else
return false;
}
//返回上一层目录
bool ReturnParentDir() {
if (m_curDir->FindParent() != NULL) {
m_curDir = m_curDir->FindParent();
m_curdir = m_curDir->GetName();
LogPath(m_curDir);
if (m_curdir != "/")
cout << "/";
cout << endl;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
//进入子目录
bool EnterChildDir(string dirName) {
if (IsDirExit(dirName)) {
m_curDir = m_curDir->FindDir(dirName);
m_curdir = m_curDir->GetName();
LogPath(m_curDir);
cout << "/" << endl;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
//移除子目录
bool RemoveDir(string dirName) {
Node* n = m_curDir->FindDir(dirName);
if (n != NULL) {
m_curDir->Remove(n);
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
//移除文件
bool RemoveFile(string fileName) {
Node* n = m_curDir->FindFile(fileName);
if (n != NULL) {
m_curDir->Remove(n);
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
};
class Command {
public:
virtual ~Command() {}
virtual bool execute(TerminalEnv& env) = 0;
virtual bool undo(TerminalEnv& env) {
return true;
}
};
class AddDirCommand : public Command {
public:
AddDirCommand(string dirName) :_dirName(dirName) {};
bool execute(TerminalEnv& env) {
if (!env.IsDirExit(_dirName)) {
env.AddDir(_dirName);
return true;
}
else {
cout << "File exists." << endl;
return false;
}
}
bool undo(TerminalEnv& env) {
if (env.RemoveDir(_dirName)) {
cout << "Dir " << _dirName << " removed." << endl;
return true;
}
else {
cout << "None." << endl;
return false;
}
}
private:
string _dirName;
};
class CDCommand : public Command {
public:
CDCommand(string dirName) {
if (dirName == "..") {
_returnParentDir = true;
}
else {
_returnParentDir = false;
_dirName = dirName;
}
};
bool execute(TerminalEnv& env) {
//返回上一层目录
if (_returnParentDir) {
_dirName = env.GetCurDirName();
if (env.ReturnParentDir()) {
return true;
}
else {
cout << "No such dir." << endl;
return false;
}
}
//进入子目录
else {
if (env.EnterChildDir(_dirName)) {
return true;
}
else {
cout << "No such dir." << endl;
return false;
}
}
}
bool undo(TerminalEnv& env) {
//撤销返回上一层的操作
if (_returnParentDir) {
env.EnterChildDir(_dirName);
}
//撤销进入子目录的操作
else {
env.ReturnParentDir();
}
return true;
}
private:
bool _returnParentDir;
string _dirName;
};
class AddFileCommand : public Command {
public:
AddFileCommand(string fileName) :_fileName(fileName) {};
bool execute(TerminalEnv& env) {
if (!env.IsFileExit(_fileName)) {
env.AddFile(_fileName);
return true;
}
else {
cout << "File exists." << endl;
return false;
}
}
bool undo(TerminalEnv& env) {
if (env.RemoveFile(_fileName)) {
cout << "File " << _fileName << " removed." << endl;
return true;
}
else {
cout << "None." << endl;
return false;
}
}
private:
string _fileName;
};
class MacroCommand :public Command {
private:
vector<Command*> commands;
public:
void AddCommand(Command *c) { commands.push_back(c); }
bool execute(TerminalEnv& env) {
if (commands.empty()) {
cout << "None." << endl;
return false;
}
auto it = commands.end() - 1;
Command* c = *it;
c->undo(env);
commands.pop_back();
return true;
}
};
int main() {
int m;
cin >> m;
TerminalEnv te;
MacroCommand undoCommand;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
// 处理各个命令
string c, str;
cin >> c;
Command* command;
if (c.find("addfile", 0) != string::npos) {
cin >> str;
command = new AddFileCommand(str);
if (command->execute(te)) {
undoCommand.AddCommand(command);
}
}
else if (c.find("adddir", 0) != string::npos) {
cin >> str;
command = new AddDirCommand(str);
if (command->execute(te)) {
undoCommand.AddCommand(command);
}
}
else if (c.find("cd", 0) != string::npos) {
cin >> str;
command = new CDCommand(str);
if (command->execute(te)) {
undoCommand.AddCommand(command);
}
}
else {
undoCommand.execute(te);
}
}
return 0;
}
第三道:
使用暴力法,每将x+1,计算经过多少个格子,若此时的y为整数,则代表到了一个整点。
结果:AC10%,超时。暂未有其他好的思路。
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
long MOD = 998244353;
int fun(double y1, double y2) {
int n;
n = (int)(ceil(y2) - floor(y1));
return n;
}
int main(void)
{
int d, k;
cin >> d >> k;
double x = 1;
double y1 = sqrt((pow(x, 2) - 1) / d);
++x;
int res = 0;
while (k != 0)
{
double y2 = sqrt((pow(x, 2) - 1) / d);
if (y2 - (int)y2 == 0) {
--k;
}
res += fun(y1, y2);
y1 = y2;
++x;
}
cout << res % MOD << endl;
return 0;
}
第四道
主要考察向量的计算,包括向量的点乘、叉乘、向量相加、相减、取模等操作。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
void PrintVec(const float* v) {
printf("%.3f %.3f %.3f\n", v[0], v[1], v[2]);
}
void ScanfVec(const float* v) {
scanf("%f %f %f", v, v + 1, v + 2);
}
void Shading(const float* Ks, const float* lightColor,
const float* normal, const float* lightDir, const float* position,
const float* eyePos, float specularPower, float* specColor) {
//写下你的代码
float V[3], H[3];
V[0] = eyePos[0] - position[0];
V[1] = eyePos[1] - position[1];
V[2] = eyePos[2] - position[2];
float eMinsP = sqrt(V[0] + V[1] + V[2]);
V[0] /= eMinsP;
V[1] /= eMinsP;
V[2] /= eMinsP;
H[0] = lightDir[0] + V[0];
H[1] = lightDir[1] + V[1];
H[2] = lightDir[2] + V[2];
float hPlusV = sqrt(H[0] + H[1] + H[2]);
H[0] /= hPlusV;
H[1] /= hPlusV;
H[2] /= hPlusV;
float tmp = max(normal[0] * H[0] + normal[1] * H[1] + normal[2] * H[2], (float)0);
tmp = pow(tmp, specularPower);
specColor[0] = Ks[1] * lightColor[2] - Ks[2] * lightColor[1];
specColor[1] = Ks[2] * lightColor[0] - Ks[0] * lightColor[2];
specColor[2] = Ks[0] * lightColor[1] - Ks[1] * lightColor[0];
specColor[0] *= tmp;
specColor[1] *= tmp;
specColor[2] *= tmp;
}
int main()
{
int numCase = 0;
scanf("%d", &numCase);
float S[3], C[3], N[3], L[3], P[3], E[3], m;
float specColor[3];
for (int i = 0; i < numCase; i++){
ScanfVec(S);
ScanfVec(C);
ScanfVec(N);
ScanfVec(L);
ScanfVec(P);
ScanfVec(E);
scanf("%f", &m);
Shading(S, C, N, L, P, E, m, specColor);
PrintVec(specColor);
}
return 0;
}
结果:0%。后在论坛上看到S*C处,叉乘是错误的,改为点乘就100%了。emmmm我觉得吧,这道题没AC应该不算我的锅吧….
第五题
该题其实就是求图上每两个顶点之间的最短路径,用Floyd算法可以解决。
难点在于顶点之间的长度还会更新,若直接用Floyd算法重新计算最短路径,感觉会超时,毕竟时间复杂度达到了O(k*n^3),有一个小小优化的思路就是,若更新的长度小于之前的长度,则不更新最短路径,最后也因时间问题没写就交卷了。